Material Properties
Material properties are defined on the Material Properties Spreadsheet and then are referred to as you build section sets, members, and plates.
You can perform analysis using any type of material; simply define the
properties for the material here. You can use up to 500 materials
in a single model although most models will only have one or two.
Material Properties Spreadsheet
The Material Properties spreadsheet records the material properties to be used in the model
and can be accessed by selecting Materials
Click on image to enlarge it
 button on the
button on the
Material Properties Spreadsheet - Columns
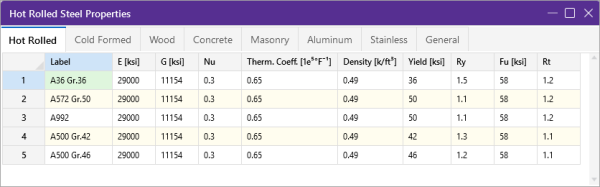
Hot Rolled Specific Material Data
The Hot Rolled tab records a number of hot rolled steel specific material properties that do not exist for the other materials. These entries are described below:
Click on image to enlarge it
Hot Rolled Specific Material Data
|
Column |
Description |
|---|---|
| Ry |
The ‘Ry’ column displays the ratio of the expected yield stress to the specified minimum yield stress. This value is used in determining the required strength of an element for the seismic detailing checks. |
| Fu |
The ‘Fu’ column displays the specified minimum tensile strength. This value is used per AISC 358 to calculate Cpr which is in turn used to calculate the probable maximum moment at a plastic hinge in the seismic detailing calculations. |
| Rt |
The ‘Rt’ column is currently not used by the program. In a future version of the program this value will be used to calculate the expected tensile strength for the seismic detailing checks. |
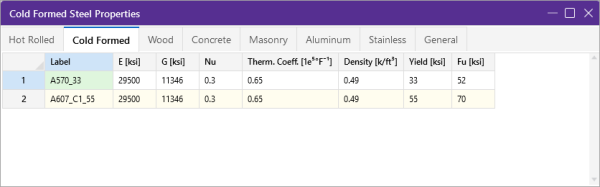
Cold Formed Specific Material Data
The Cold Formed tab records a cold formed material property that may not exist for the other materials. This entry is described below:
Click on image to enlarge it
Cold Formed Specific Material Data
|
Column |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Fu (Ultimate) |
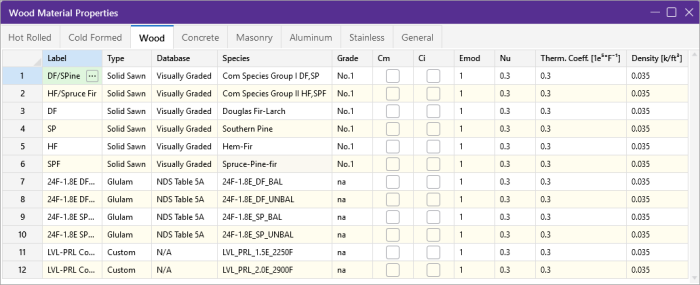
Wood Specific Material Data
The Wood tab records a number of wood specific material properties that do not exist for the other materials. These entries are described below:
Click on image to enlarge it
Wood Specific Material Data
Commercial Species Groups
When either the NDS 05/08, 12, 15, 18, or 24 wood design code is selected, the Solid Sawn Species menu lists two new species listed that are not specifically shown in the NDS code. These are the Commercial Species Group I - DF/SP and Commercial Species Group II - HF/SPFe Fir. These are meant to be simplified groupings of the most commonly used wood species. It is meant to simplify the selection procession for wood member design in the United States.
The design values for Group I take the NDS allowable stress values for two of the most widely used species (Doug Fir-Larch and Southern Pine) and uses the lower bound allowable stress value for each size and grade.
Similarly, the design values for Group II take the allowable stress values for Hem Fir and Spruce-Pine-Fir and use the lower bound allowable stress values for each size and grade.
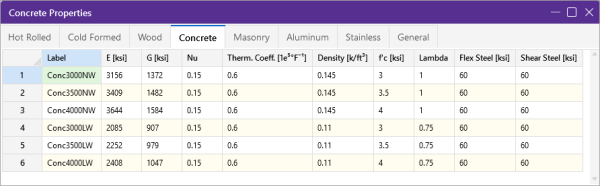
Concrete Specific Material Data
The Concrete tab records a few concrete specific material properties that do not exist for the other materials. These entries are described below:
Click on image to enlarge it
Concrete Specific Material Material Data
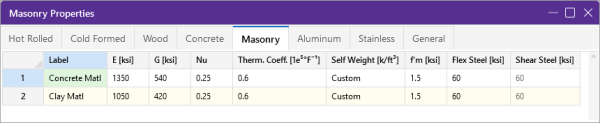
Masonry Specific Material Data
The Masonry tab records masonry specific material properties. Here we describe items that do not exist for other materials.
Click on image to enlarge it
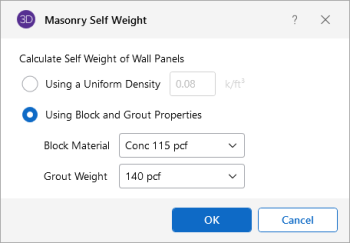
Masonry Self Weight can be accounted for by two different methods. Entering a number for the density will result in masonry walls which have a self weight equal to that density multiplied by the wall cross-sectional area. Otherwise, click within the cell to launch the masonry self weight dialog:
Click on image to enlarge it
Set the Using Block and Grout Properties option to have the program automatically calculate the self weight of the wall using the weights from tableB3 of the Reinforced Masonry Engineering Handbook (RMEH). The self weight will be listed as Custom.
Masonry Specific Material Data
- Masonry Shear Steel is automatically set to the Flex steel strength.
- Masonry materials are used only for walls in wall footings. See the Wall Footing Definitions spreadsheet for more information.
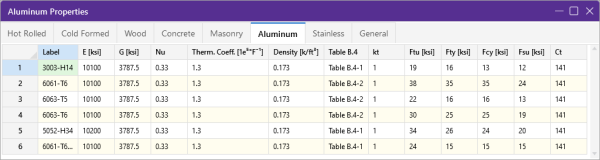
Aluminum Specific Material Data
The Aluminum tab records a number of aluminum specific material properties that do not exist for the other materials. These entries are described below:
Click on image to enlarge it
Aluminum Specific Material Data
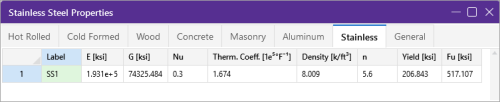
Stainless Steel Specific Material Data
The Stainless tab records stainless steel material properties. These entries are described below:
Click on image to enlarge it
Stainless Steel Specific Material Data
|
Column |
Description |
|---|---|
| n |
The ‘n’ column displays the specified Ramberg Osgood parameter used for determining secant modulus. See AISC DG27 Table 6-1. |
| Yield |
The Yield column displays the specified yield stress. |
| Fu |
The ‘Fu’ column displays the specified ultimate tensile stress. |
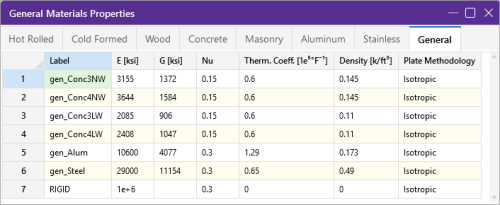
General Material Data
The General tab records general material properties. These entries are described below:
Click on image to enlarge it
Cold Formed Specific Material Data
|
Column |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Plate Methodology |
The Plate Methodology column displays the behavior to use for plate analysis: isotropic or orthotropic. For more information, see Orthotropic Behavior. |
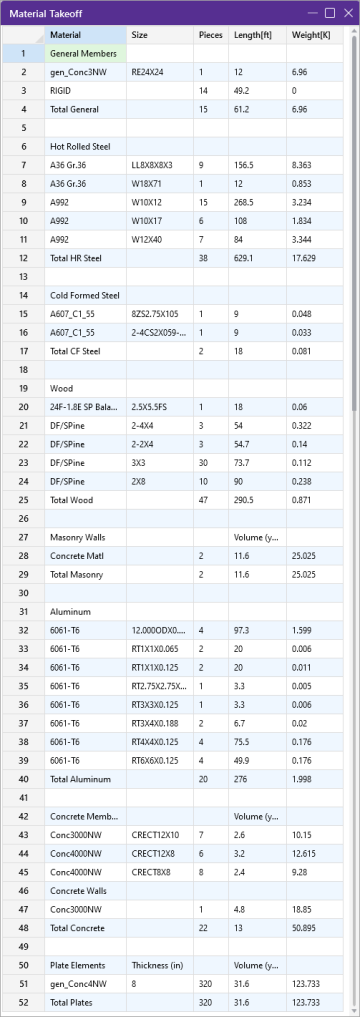
Material Take-Off
Access the Material Take-Off spreadsheet by selecting it from the Results menu.
Click on image to enlarge it
This spreadsheet shows material takeoff information for each material and
For Concrete members
- This material takeoff report is independent of the loads applied to the model, i.e. the applied loads do not influence this report.
- The number of pieces is reflective of the number of members of a particular size. For example, one double angle will be counted as one piece, with the length being the member length, and the weight being that of the double angle.
- Plates are also included in the Material Take-Off.